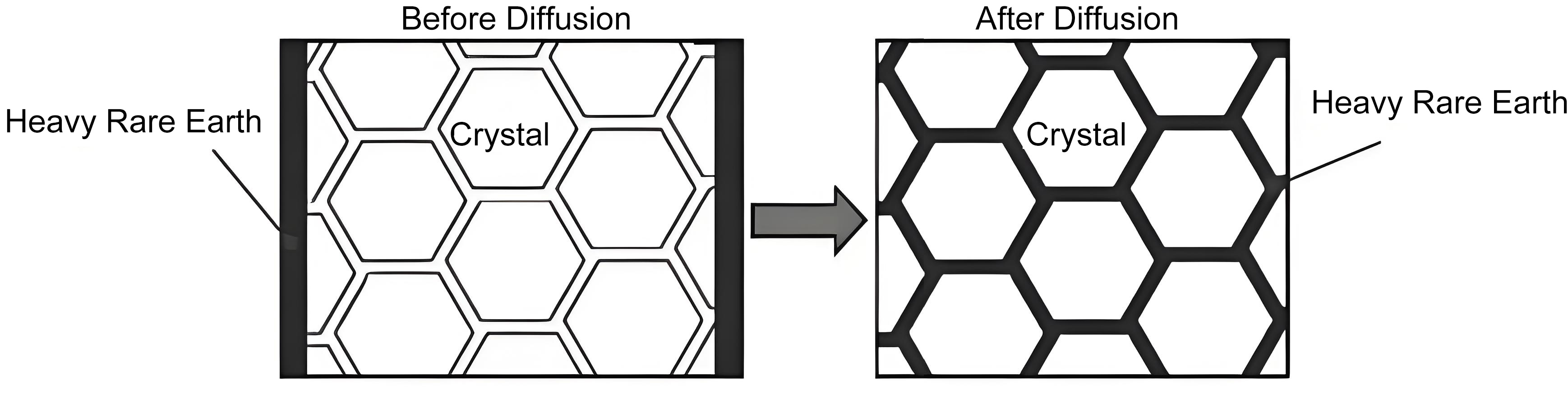
SC Grain Refinement Core Control Process
HD Intergranular Crushing
JM Fine-Grain Grinding Low-Grain Powder Production
Sintering Grain Control Low-Temperature Long-Time Sintering Process
Fine Grain Magnet
| Traditional Technology | GRF-1 | GRF-2(Current) | GRF-3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
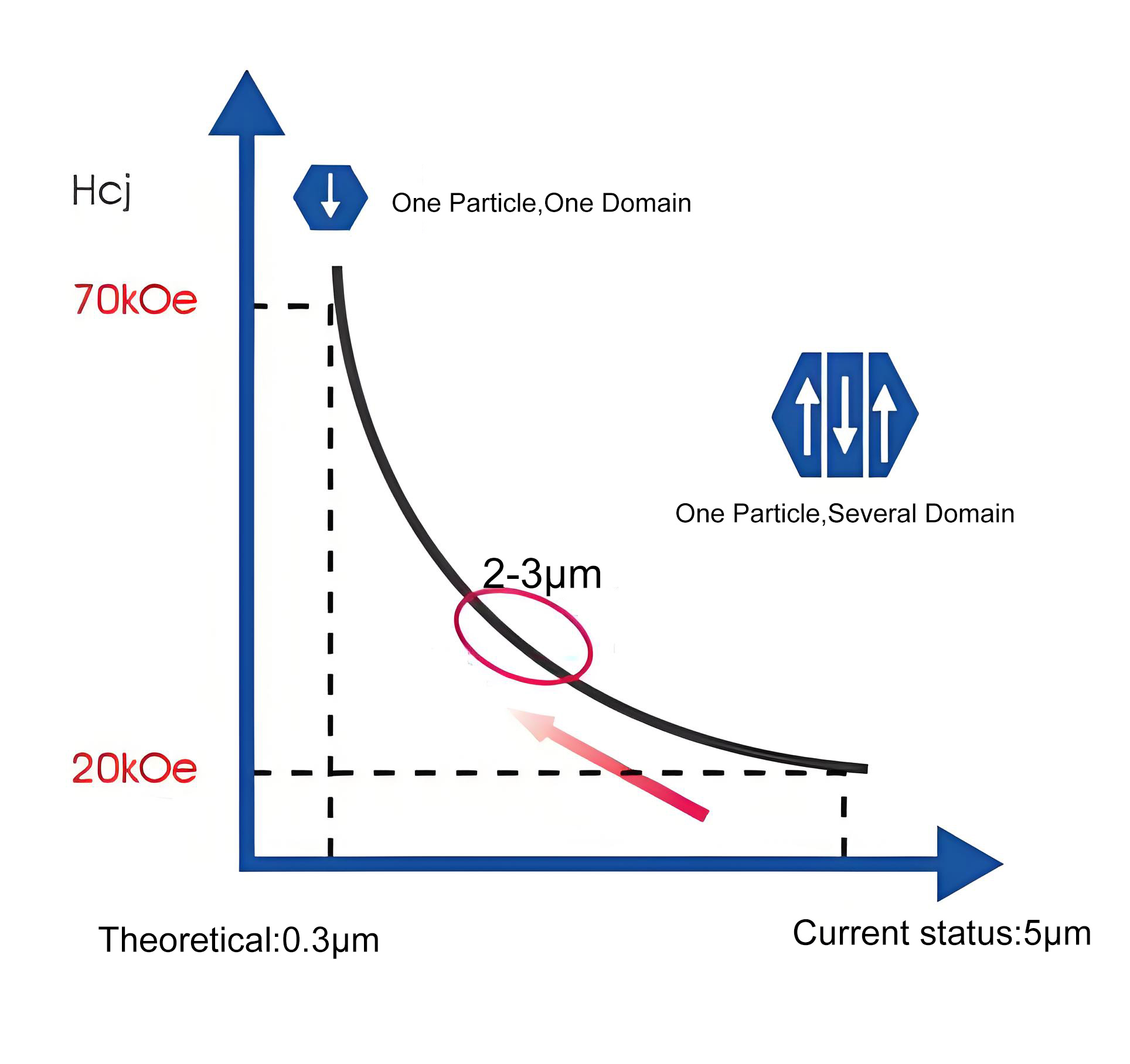
| Grain Size (μm) | 6-10 | 5-8 | 3-6 | 2-3 |
| Powder Size (μm) | 3-5 | 2.5-3.5 | 2-3 | 1-1.5 |